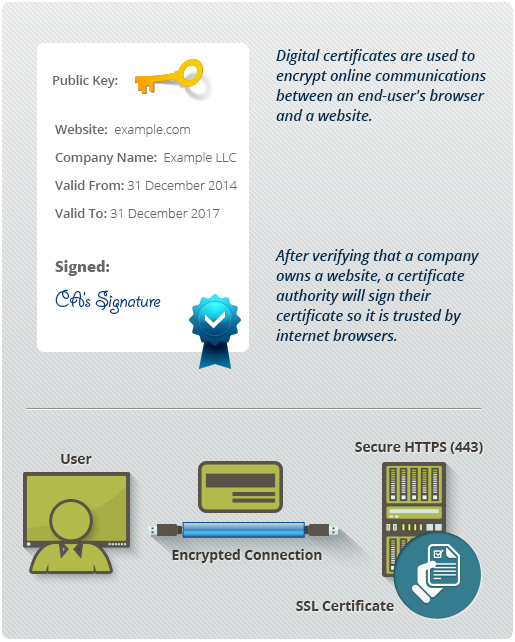
What is a Digital Certificate?
A Digital Certificate is an electronic "password" that allows a person, organization to exchange data securely over the Internet using the public key infrastructure (PKI). Digital Certificate is also known as a public key certificate or identity certificate.
Technology Overview of Digital Certificates
This guide is a brief introduction to Digital Certificate and PKI technologies.
Digital Certificates are a means by which consumers and businesses can utilize the security applications of Public Key Infrastructure (PKI). PKI comprises the technology to enable secure e-commerce and Internet-based communication.
Why is security needed on the Internet?
The number of people and businesses online is continuing to increase. As access becomes faster and cheaper such people will spend even more time connected to the Internet for personal communication and business transactions.
The Internet is an open communications network that was not originally designed with security in mind. Criminals have found they can exploit its vulnerabilities for fraudulent gain. If the Internet is to succeed as a business and communications tool users must be able to communicate securely.
What does Digital Certificate security provide?
Identification / Authentication:
The persons/entities with whom we are communicating are really who they say they are.
Confidentiality:
The information within the message or transaction is kept confidential.
It may only be read and understood by the intended sender and receiver.
Integrity:
The information within the message or transaction is not tampered with accidentally or deliberately en route without all parties involved being aware of the
tampering.
Non-Repudiation:
The sender cannot deny sending the message or transaction, and the receiver
cannot deny receiving it.
Access Control:
Access to the protected information is only realized by the intended person
or entity.
All the above security properties can be achieved and implemented through the
use of Public Key Infrastructure (in particular Digital Certificates).
Next >